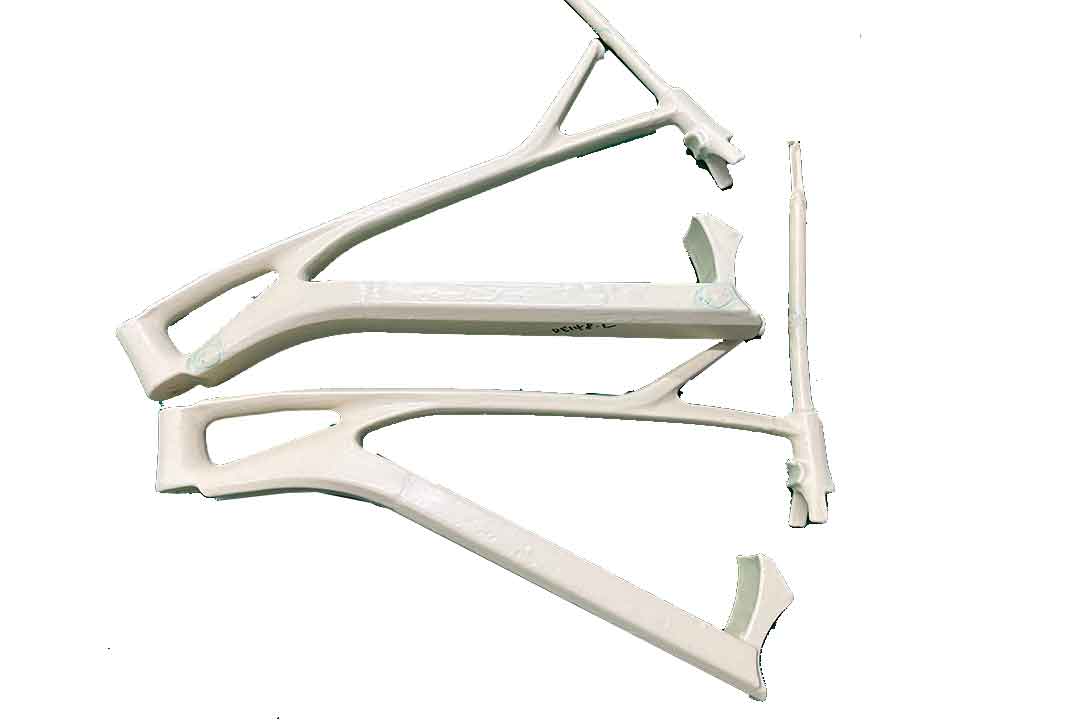
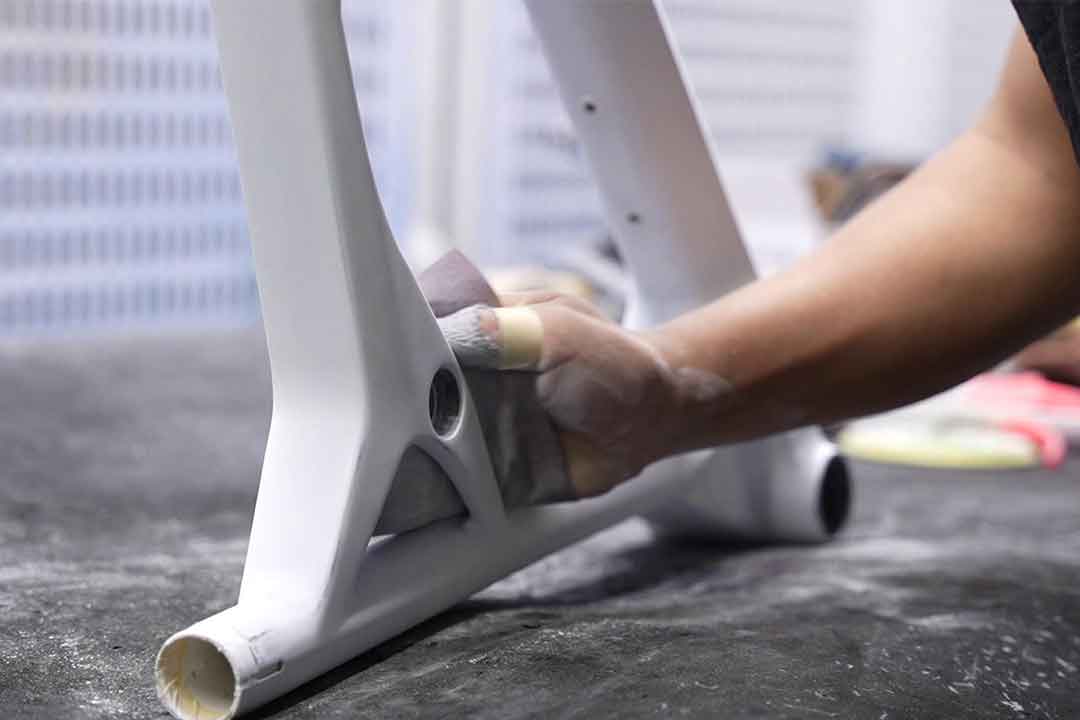
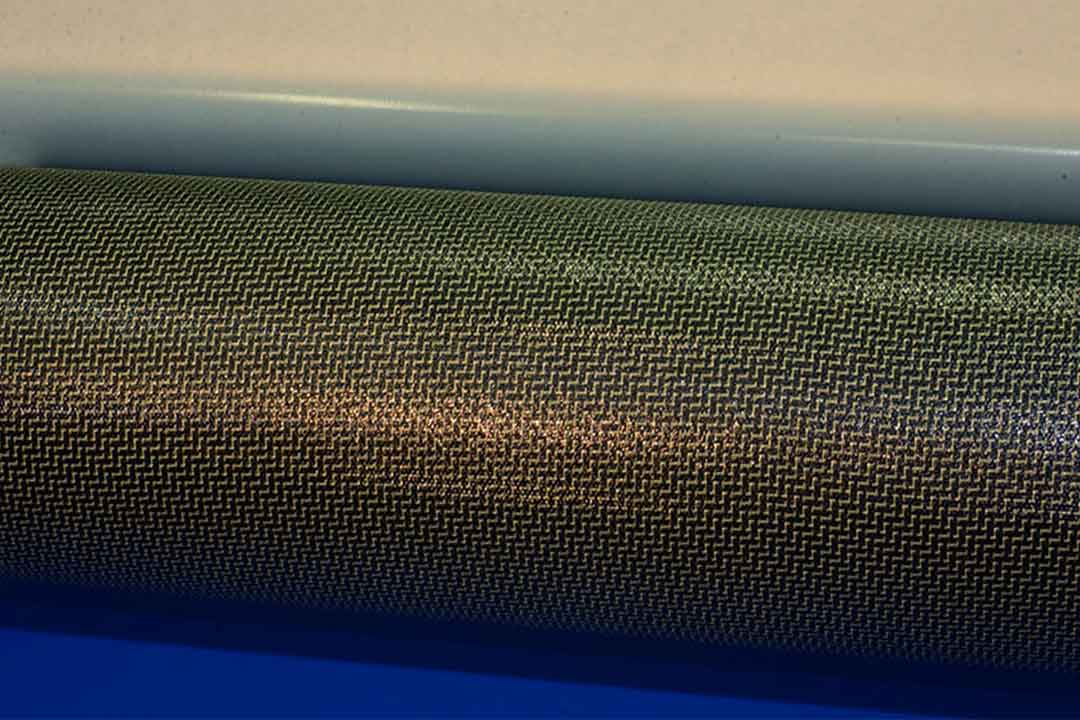
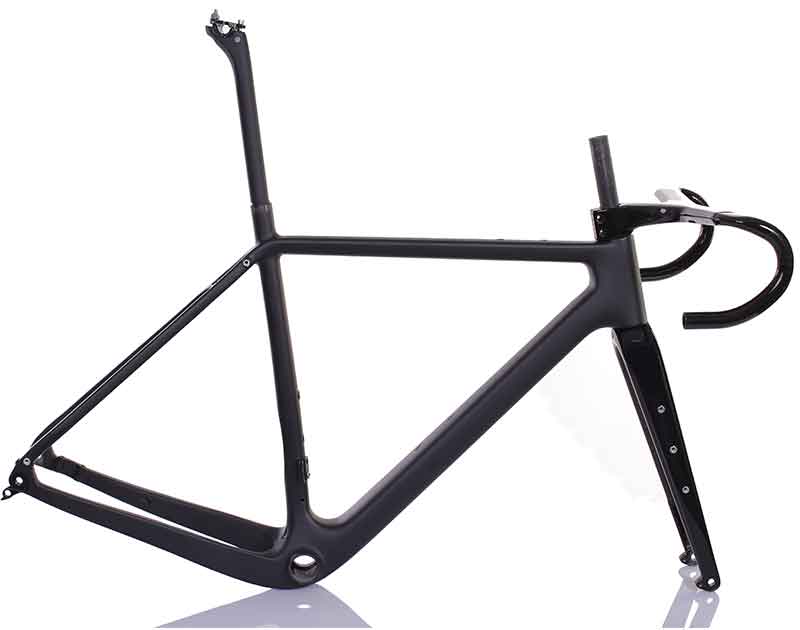
Welcome to Mondince Bike - A well-known factory specialized in produce carbon bike frame and other parts since 2007.
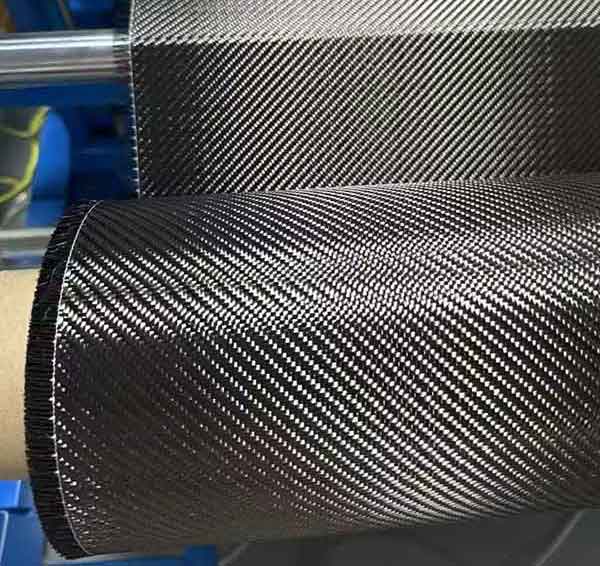
wet and dry carbon
Carbon fiber is a material that has revolutionized various industries due to its incredible strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. However, not all carbon fibers are created equal. When it comes to carbon fiber products, you might have heard the terms "wet carbon" and "dry carbon." But what do these terms mean, and how do they differ? This article will delve into the properties, manufacturing processes, and applications of wet and dry carbon to give you a comprehensive understanding.
Before diving into wet and dry carbon, let's first understand what carbon fiber is. Carbon fiber is composed of carbon atoms bonded together in a crystalline formation. This structure provides the fibers with exceptional strength while maintaining an incredibly low weight. The crystalline structure is a crucial aspect, as it gives carbon fiber its distinct mechanical properties.
The production of carbon fiber involves several intricate steps. Initially, precursor materials such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN) or pitch are subjected to high-temperature processes to create carbon fibers. These fibers are then woven together to form fabrics or combined with resins to produce composite materials. The choice of precursor and manufacturing process can significantly influence the characteristics of the final product.
Carbon fiber's unique properties make it ideal for a wide range of applications. In the automotive industry, it's used to create lightweight yet sturdy vehicle components. In aerospace, carbon fiber contributes to fuel efficiency by reducing aircraft weight. Additionally, it's utilized in sporting goods, medical equipment, and even in the construction of high-performance bicycles.
Wet carbon, also known as wet-lay carbon, refers to carbon fiber products made using a wet-layup process. In this method, carbon fiber fabric is manually placed into a mold, and a resin is applied over it. The resin, usually epoxy, binds the fibers together and hardens to form a solid structure once cured. The manual nature of this process allows for customization and flexibility in design.
The wet-layup process is relatively straightforward. After preparing the mold, carbon fiber fabric is layered into it. The resin is then carefully applied to ensure thorough saturation of the fibers. Once the resin has been applied, the component is left to cure, either at room temperature or with the assistance of heat. This process can be labor-intensive but offers significant flexibility for creating complex shapes.
Wet carbon is known for its flexibility and ease of manufacturing. The wet-layup process allows for a wide variety of shapes and sizes, making it suitable for custom applications. However, wet carbon typically has a higher resin content, which can make it heavier and less strong compared to its dry carbon counterpart. The increased resin can also affect the aesthetic finish of the product, often resulting in a less uniform appearance.
Wet carbon is commonly used in applications where cost and ease of production are more critical than weight savings and ultimate strength. Some typical uses include:
- Automotive Body Panels: Often used in aftermarket parts where aesthetics and cost are more important than performance.
- Boat Hulls: The flexibility of wet carbon makes it ideal for the unique shapes required in marine applications.
- Sporting Goods: Items like surfboards and recreational equipment benefit from the customizability and cost-effectiveness of wet carbon.
Dry carbon, also known as pre-preg carbon, is a type of carbon fiber product made using pre-impregnated carbon fiber fabric. In this process, the carbon fiber fabric is pre-impregnated with a specific amount of resin, which is partially cured. The pre-preg sheets are then laid into a mold and fully cured under heat and pressure, resulting in a highly consistent and high-quality finish.
The manufacturing process for dry carbon involves precise control over resin application. Pre-preg carbon fiber sheets are prepared with resin content optimized for performance. These sheets are then placed into molds and subjected to controlled heat and pressure, ensuring thorough curing and bonding. This method minimizes excess resin and results in a superior strength-to-weight ratio.
Dry carbon is renowned for its superior strength-to-weight ratio. The controlled resin content leads to lighter and stronger products. The manufacturing process ensures a consistent finish and precise resin distribution, making dry carbon ideal for high-performance applications. The result is a material that not only performs exceptionally but also offers a sleek, professional appearance.
Due to its high strength and low weight, dry carbon is often used in applications where performance is crucial. Some examples include:
- Aerospace Components: Essential for reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity in aircraft.
- High-Performance Automotive Parts: Used in race cars and performance vehicles where every gram matters.
- Racing Equipment: Critical in motorsports for components like chassis, wheels, and aerodynamic elements.
Understanding the differences between wet and dry carbon is essential when choosing the right material for your needs.
- Wet Carbon: Made using a manual wet-layup process. This allows for customization but may lack the precision of dry carbon methods.
- Dry Carbon: Made using pre-impregnated carbon fiber and requires curing under heat and pressure. This process offers precision and consistency in the final product.
- Wet Carbon: Higher resin content, making it heavier. This can affect both the weight and the structural properties of the material.
- Dry Carbon: Lower, controlled resin content, resulting in a lighter product. The precision in resin application ensures optimal strength-to-weight performance.
- Wet Carbon: Generally lower strength-to-weight ratio. While sufficient for many applications, it may not meet the demands of high-performance needs.
- Dry Carbon: Superior strength-to-weight ratio due to optimized resin distribution. Ideal for applications where maximum efficiency and performance are required.
- Wet Carbon: More affordable due to simpler manufacturing. The trade-off is often in performance and weight.
- Dry Carbon: More expensive but offers higher performance. The investment is justified in applications where the benefits of reduced weight and increased strength are critical.
When deciding between wet and dry carbon, consider the following factors:
- Wet Carbon: More budget-friendly, suitable for projects with cost constraints.
- Dry Carbon: A premium option, justifiable in projects where performance gains outweigh the cost.
- Wet Carbon: Ideal for applications where customization and budget are priorities.
- Dry Carbon: Best suited for high-performance needs where every gram of weight saving can lead to significant advantages.
- Wet Carbon: Simpler manufacturing process, accessible for a wider range of producers.
- Dry Carbon: Requires specific curing processes, potentially limiting its use to facilities equipped with the necessary technology.
Both wet and dry carbon have their unique advantages and applications. Wet carbon is suitable for projects where cost and ease of manufacturing are prioritized, while dry carbon excels in high-performance applications where strength and weight are critical. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Whether you're in the automotive industry, aerospace, or any other field that requires advanced materials, carbon fiber offers versatile solutions. By choosing the right type of carbon fiber, you can ensure your projects achieve the desired balance of performance, cost, and manufacturability.
As technology advances, the applications and efficiency of carbon fiber continue to grow. Innovations in manufacturing processes and material composition promise to enhance the properties and reduce the costs of both wet and dry carbon, expanding their potential uses across industries.
Ultimately, the choice between wet and dry carbon should align with your project's specific needs and constraints. By understanding the nuances of each type, you can select the most appropriate material to achieve optimal results.