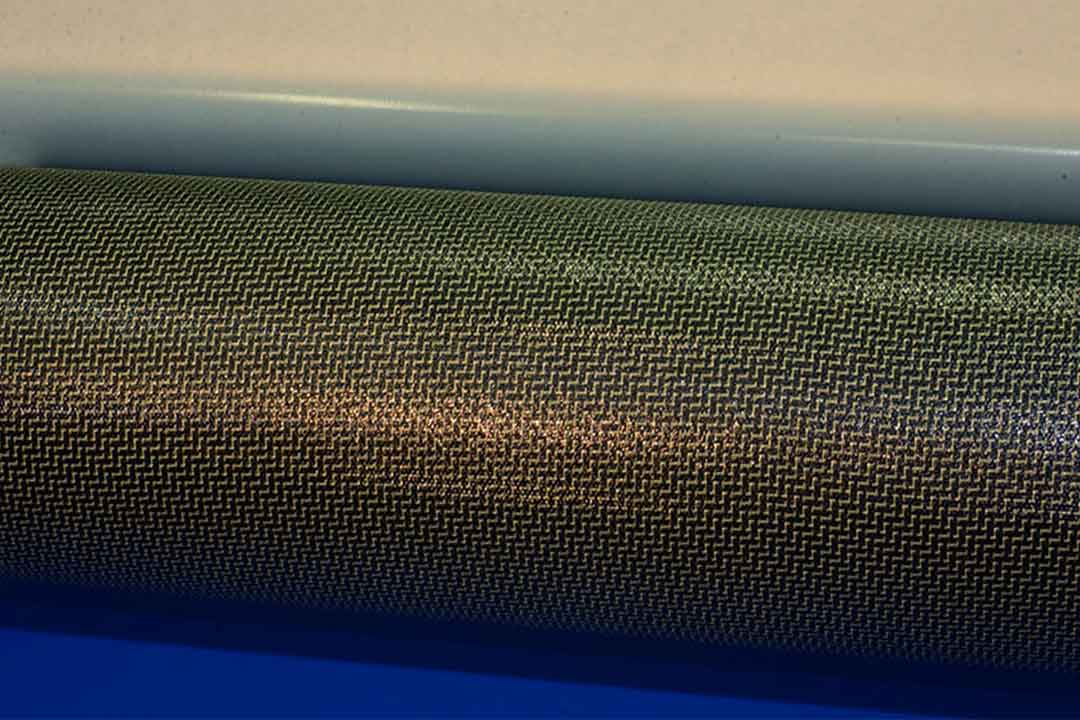
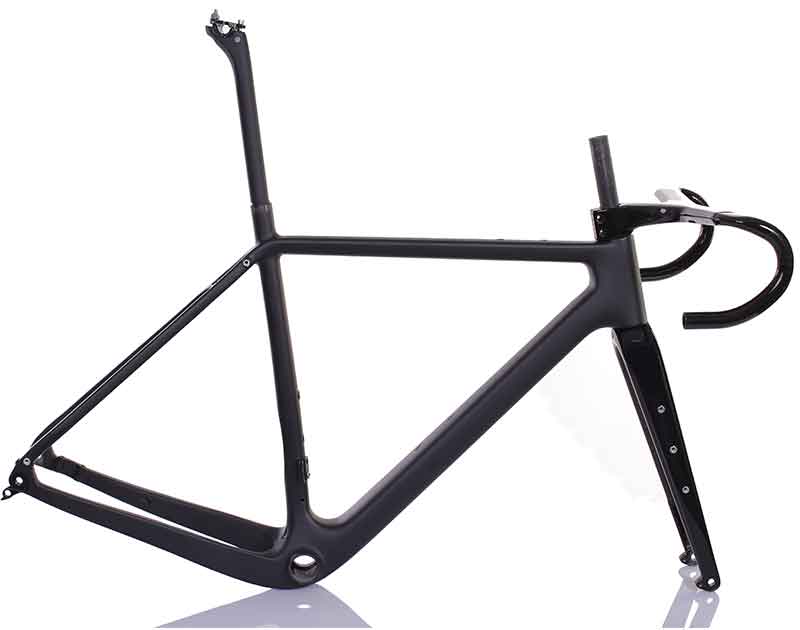
Welcome to Mondince Bike - A well-known factory specialized in produce carbon bike frame and other parts since 2007.
Innovations in Carbon Fiber Applications Today
In recent years, carbon fiber has emerged as a revolutionary material, transforming industries with its unique properties. Known for its strength, lightweight nature, and durability, carbon fiber is increasingly being used in innovative ways. This article explores the advancements in carbon fiber applications and how they are reshaping various sectors.

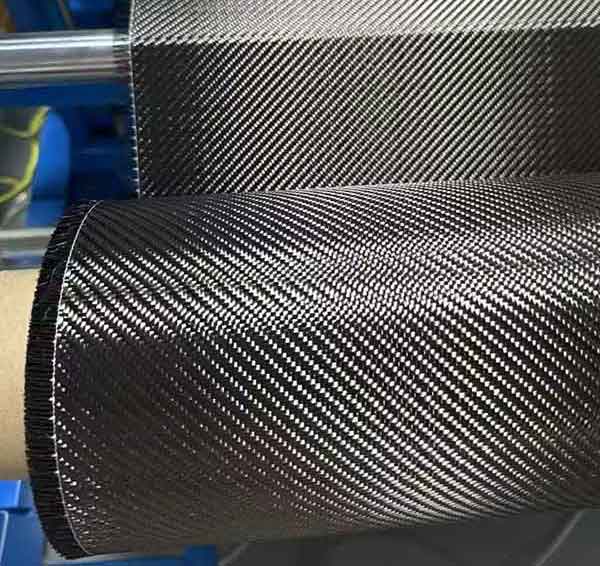
Carbon fiber is a strong, lightweight material composed of thin, strong crystalline filaments of carbon that are used to strengthen other materials. The fibers are often combined with other materials to create a composite material. The primary advantage of carbon fiber is its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it a favorite in industries where weight reduction is crucial.
Composition and Structure
Carbon fiber is primarily made of carbon atoms bonded together in a crystalline formation. This structure gives the fiber its exceptional strength and rigidity. The production process involves the oxidation and carbonization of precursor materials, typically polyacrylonitrile (PAN) or pitch. The transformation from organic fibers to carbon fibers involves several stages of heating and stretching, culminating in a material that is both incredibly strong and extremely lightweight.
Types of Carbon Fiber
There are several types of carbon fiber, each suited for different applications. High modulus fibers offer maximum stiffness, making them ideal for aerospace and high-performance sports equipment. Standard modulus fibers, on the other hand, are more cost-effective and are used in automotive and industrial applications. Intermediate modulus fibers strike a balance between strength and flexibility, useful in a wide array of sectors.
Carbon Fiber Composites
The true potential of carbon fiber is realized when it is used as a composite material. By combining carbon fibers with other materials like epoxy resins, manufacturers can tailor the mechanical properties to meet specific needs. These composites are especially valued for their ability to maintain strength while significantly reducing weight, which is why they are so prevalent in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Advancements in Carbon Fiber Technology
Enhanced Manufacturing Processes
One of the major advancements in the carbon fiber industry is the improvement in manufacturing processes. Techniques such as automated fiber placement (AFP) and resin transfer molding (RTM) have increased production efficiency and lowered costs. These advancements allow for more complex designs and broader applications.
Automated Fiber Placement (AFP)
AFP involves the use of robotic systems to lay down carbon fiber with precision and speed. This automation reduces human error and increases the consistency of the product. By utilizing AFP, manufacturers can produce intricate components with varying geometries, optimizing the material's properties for specific uses. The reduction in labor costs also makes this method economically viable for large-scale production.
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
RTM is a process that involves injecting resin into a mold containing a carbon fiber preform. This technique ensures thorough impregnation of the fibers, resulting in a composite with superior mechanical properties. RTM is particularly advantageous for producing large, complex shapes that would be difficult to achieve with other methods. This versatility opens new avenues for carbon fiber applications in industries like automotive and wind energy.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is revolutionizing the way carbon fiber composites are made. By depositing layers of carbon fiber-infused material, manufacturers can create lightweight, high-strength components with minimal waste. This method allows for rapid prototyping and customization, making it an attractive option for industries looking to innovate quickly.
Sustainable Carbon Fiber Production
With growing environmental concerns, there's been a push towards sustainable carbon fiber production. Innovations in recycling processes and the development of bio-based carbon fibers are paving the way for more eco-friendly solutions. These methods reduce waste and energy consumption, making carbon fiber a more sustainable choice.
Recycling Processes
Recycling carbon fiber is challenging due to the strength of the material, but new techniques are making it feasible. Methods like thermal and chemical recycling break down composites into reusable fibers and resins. These processes not only reduce landfill waste but also decrease the need for raw materials, making carbon fiber production more sustainable.
Bio-based Carbon Fibers
Researchers are exploring the use of natural precursors like lignin, a byproduct of the paper industry, to produce carbon fibers. This approach reduces reliance on petroleum-based materials and lowers the carbon footprint of the production process. Bio-based carbon fibers are still in the development stage, but they hold promise for a greener future in industries that depend heavily on carbon composites.
Energy-efficient Manufacturing
Efforts to reduce the energy consumption of carbon fiber production are also underway. Innovations in process optimization and the use of renewable energy sources are helping to lower the environmental impact. By adopting these practices, manufacturers can produce carbon fiber more sustainably, aligning with global initiatives to combat climate change.
Modern Applications of Carbon Fiber
Aerospace and Aviation
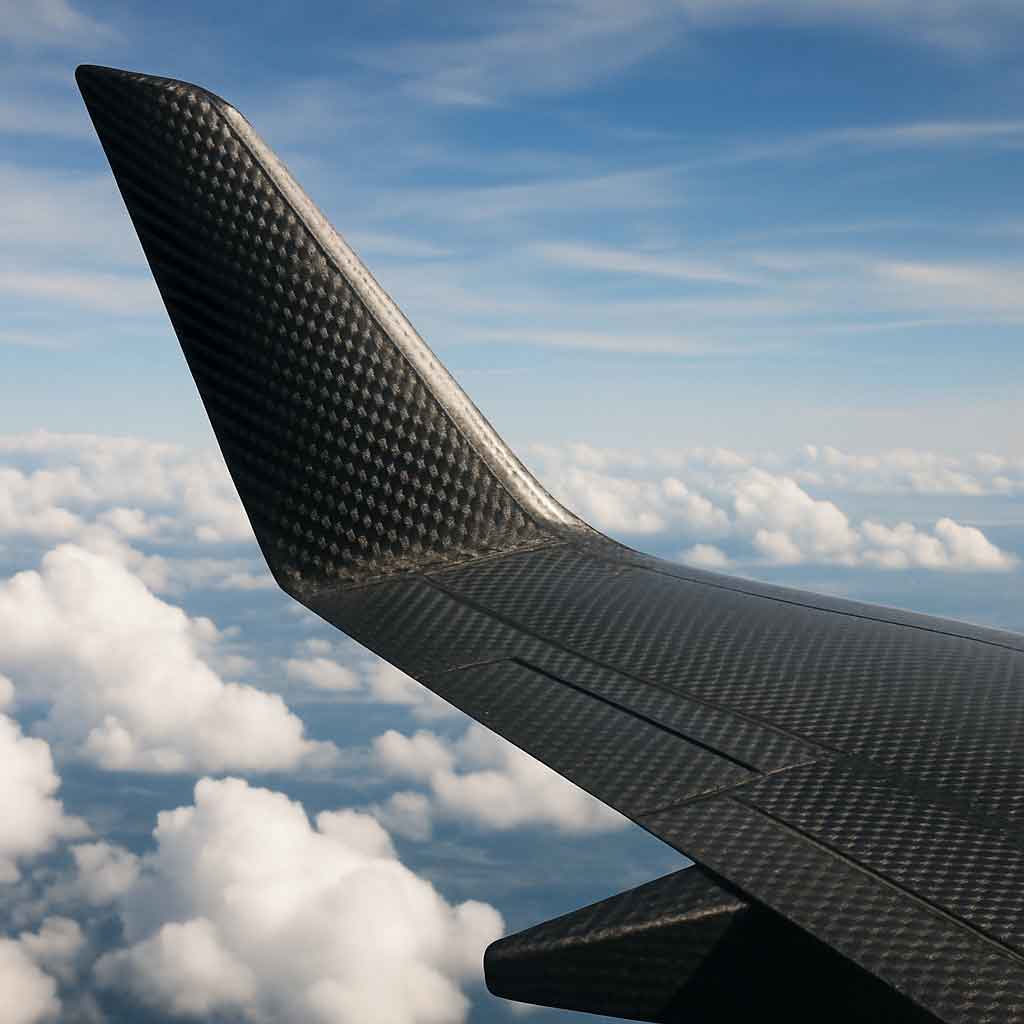

In the aerospace industry, carbon fiber is a game-changer. Its lightweight properties contribute to fuel efficiency and increased payload capacity. Aircraft manufacturers use carbon fiber composites in wings, fuselages, and interior components. These innovations not only enhance performance but also reduce maintenance costs.
Aircraft Design and Performance
Carbon fiber allows for more aerodynamic designs due to its strength and flexibility. Engineers can create complex shapes that reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency. The material's resistance to fatigue and corrosion also extends the lifespan of aircraft components, reducing the frequency of repairs and inspections.
Space Exploration
Carbon fiber's strength and lightweight nature make it ideal for spacecraft and satellite applications. The material can withstand the extreme conditions of space travel, protecting sensitive equipment from damage. Its use in satellite structures also allows for more payload capacity, enabling more comprehensive scientific instruments and communication devices to be launched into orbit.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
The use of carbon fiber in UAVs, or drones, has revolutionized their design and functionality. The material's lightweight properties allow for longer flight times and greater payload capacities, enhancing the capabilities of drones in surveillance, delivery, and agricultural applications. Carbon fiber also contributes to the stealth characteristics of military drones, reducing radar visibility.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector has embraced carbon fiber for its potential to improve fuel efficiency and performance. High-end sports cars, like those from Ferrari and Lamborghini, utilize carbon fiber for body panels, frames, and interior elements. The material's strength allows for thinner designs, contributing to a vehicle's speed and agility.
Mass-market Vehicles
While traditionally used in luxury cars, carbon fiber is gradually making its way into mass-market vehicles. Manufacturers are exploring hybrid materials that combine carbon fiber with other composites to reduce costs. These innovations are expected to lead to lighter, more fuel-efficient cars that appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
In the growing EV market, reducing weight is crucial for extending battery range. Carbon fiber composites are used in the construction of battery enclosures and chassis components to achieve this goal. The material's durability also enhances safety by providing superior crash resistance, an essential consideration for EV manufacturers.
Automotive Design and Customization
Carbon fiber's aesthetic appeal and versatility make it a popular choice for aftermarket customization. Car enthusiasts use carbon fiber wraps and components to enhance the look and performance of their vehicles. This trend has created a niche market, driving innovation in carbon fiber applications for automotive design.
Renewable Energy
In renewable energy, carbon fiber is used in wind turbine blades and solar panels. The material's light weight and strength allow for longer blades, which can capture more wind energy, leading to more efficient turbines. Similarly, carbon fiber's durability makes it ideal for solar panel frames, extending their lifespan.
Wind Energy
The use of carbon fiber in wind turbine blades has led to significant advancements in efficiency. Longer blades can capture more wind, generating more power without increasing the size of the turbine. The material's resistance to environmental factors also reduces the need for maintenance, lowering operational costs.
Solar Energy
Carbon fiber is also making strides in solar energy applications. Its lightweight nature enables the production of portable solar panels, expanding the range of off-grid applications. Additionally, carbon fiber's thermal stability and strength enhance the durability and efficiency of solar panel installations, contributing to the growth of solar energy as a viable renewable resource.
Tidal and Wave Energy
Emerging renewable technologies like tidal and wave energy also benefit from carbon fiber's properties. The material's resistance to corrosion and fatigue makes it ideal for marine environments, where equipment must withstand harsh conditions. Carbon fiber components in tidal turbines and wave energy converters improve efficiency and lifespan, advancing the development of these renewable energy sources.
Sports and Recreation
Carbon fiber is revolutionizing sports equipment, providing athletes with a competitive edge. Tennis rackets, bicycles, and golf clubs made from carbon fiber are lighter and more durable than traditional materials. This innovation improves athletes' performance, allowing for quicker swings and longer rides.
Competitive Sports
In competitive sports, the use of carbon fiber equipment has become a standard. Its lightweight properties allow athletes to achieve greater speed and precision. In cycling, for example, carbon fiber frames significantly reduce the weight of bicycles, enabling faster acceleration and improved handling on challenging courses.
Recreational Sports
For recreational sports enthusiasts, carbon fiber equipment offers enhanced performance and durability. The material's resilience means it can withstand the rigors of frequent use, making it a popular choice for hobbyists. From fishing rods to ski poles, carbon fiber's application in recreational sports gear continues to grow.
Innovation in Sports Technology
Carbon fiber is also driving innovation in sports technology, including wearable devices and protective gear. Its strength and flexibility make it an excellent choice for impact-resistant helmets and body armor. Additionally, carbon fiber composites are being explored for use in smart sports equipment, incorporating sensors and electronics for real-time performance tracking.
Medical Equipment

by Benson Low (https://unsplash.com/@ckbenson)
In the medical field, carbon fiber is used in prosthetics and orthotics. Its light weight and strength make it ideal for creating comfortable, durable prosthetic limbs. Additionally, carbon fiber is used in medical imaging equipment, providing a sturdy yet lightweight frame that does not interfere with imaging processes.
Prosthetics and Orthotics
Carbon fiber's properties are particularly beneficial in the design of prosthetic limbs, where weight and strength are critical factors. The material allows for more natural movement and comfort, improving the quality of life for users. In orthotics, carbon fiber braces provide support without adding unnecessary weight, aiding in mobility and rehabilitation.
Medical Imaging Equipment
In medical imaging, carbon fiber's non-magnetic nature makes it suitable for use in MRI machines and X-ray equipment. Its strength allows for the construction of lightweight tables and supports, improving patient comfort and ease of use. The material's durability also extends the lifespan of imaging equipment, reducing maintenance costs for healthcare facilities.
Surgical Instruments
The medical industry is also exploring the use of carbon fiber in surgical instruments. Its light weight and strength make it ideal for creating precise, ergonomic tools that reduce surgeon fatigue during lengthy procedures. Carbon fiber's resistance to sterilization processes further enhances its suitability for medical applications.
Future Prospects of Carbon Fiber
The future of carbon fiber looks promising, with ongoing research and development expanding its applications. As production becomes more cost-effective and sustainable, we can expect to see carbon fiber used in even more innovative ways. From architecture to electronics, the possibilities are endless.
Architecture and Construction
Architects are beginning to explore carbon fiber for building facades and structural components. Its strength and flexibility allow for innovative designs that were previously impossible. Carbon fiber's resistance to corrosion and extreme weather conditions makes it an attractive option for sustainable building projects.
Structural Innovation
Carbon fiber's strength-to-weight ratio enables architects to design structures that are both aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound. The material's flexibility allows for the creation of intricate designs and cantilevered structures that push the boundaries of traditional architecture. This innovation opens up new possibilities for iconic buildings and sustainable urban development.
Retrofitting and Restoration
In addition to new construction, carbon fiber is being used in retrofitting and restoration projects. Its lightweight nature makes it ideal for reinforcing older structures without adding significant weight. This application is particularly valuable in seismic retrofitting, where carbon fiber composites provide additional support to buildings in earthquake-prone areas.
Sustainable Building Materials
The construction industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability, and carbon fiber is playing a role in this shift. Its durability and low maintenance requirements make it a long-lasting building material. Additionally, the development of bio-based carbon fibers and recycling processes contributes to the creation of environmentally friendly construction practices.
Consumer Electronics
As electronic devices become smaller and more complex, carbon fiber offers a lightweight solution that maintains strength and durability. Manufacturers are exploring carbon fiber for use in laptops, smartphones, and other gadgets to enhance performance and longevity.
Lightweight and Durable Designs
Carbon fiber's application in consumer electronics is driven by the need for lightweight, durable devices. The material's strength allows for thinner, more portable designs without sacrificing durability. This is particularly important in smartphones and tablets, where reducing weight enhances user experience and portability.
Heat Dissipation and Thermal Management
In addition to its structural benefits, carbon fiber's thermal conductivity properties make it valuable in electronics. It can be used to manage heat dissipation in high-performance devices, ensuring optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating. This application is crucial for the performance and longevity of modern electronic gadgets.
Innovative Wearables
Wearable technology is another area where carbon fiber is making an impact. Its lightweight and flexible nature make it ideal for creating comfortable, stylish wearables that integrate seamlessly with everyday life. From fitness trackers to smart glasses, carbon fiber composites are driving innovation in the wearable tech industry.
Challenges in the Carbon Fiber Industry
Despite its advantages, the carbon fiber industry faces challenges. High production costs and limited availability of raw materials are significant hurdles. However, ongoing advancements in production techniques and recycling methods are likely to address these issues, making carbon fiber more accessible.
Cost Reduction Strategies
Reducing the cost of carbon fiber production is a primary focus for the industry. Innovations in manufacturing processes, such as automation and additive manufacturing, are helping to lower costs. Additionally, the development of hybrid composites that use less expensive materials alongside carbon fiber is providing more affordable options for various applications.
Material Sourcing and Availability
The availability of raw materials for carbon fiber production is a concern, as the demand continues to rise. Efforts are underway to diversify the sources of precursor materials, including the use of bio-based alternatives. By expanding the resource base, the industry can reduce its reliance on traditional materials and ensure a stable supply.
Addressing Environmental Impact
While carbon fiber offers sustainability benefits in its applications, the production process can be energy-intensive. The industry is focusing on reducing its environmental impact through the adoption of renewable energy sources and improved recycling techniques. These efforts aim to make carbon fiber production more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
Carbon fiber's unique properties have made it a cornerstone of innovation across multiple industries. As technology advances, the applications of carbon fiber will continue to grow, offering new solutions to complex problems. Whether in aviation, automotive, or renewable energy, carbon fiber is set to remain a vital material in modern engineering and design.
By staying informed about these innovations, industries can leverage carbon fiber to enhance their products and processes, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable future. The continued research and development in carbon fiber technology promise a future where this remarkable material can help solve some of the world's most pressing challenges.